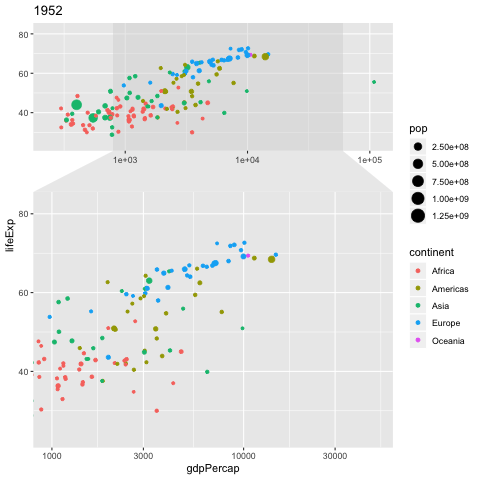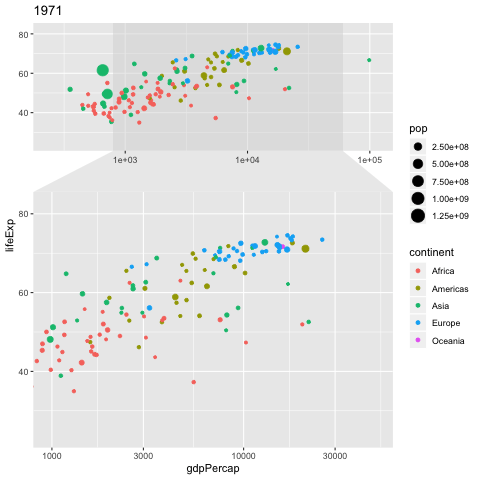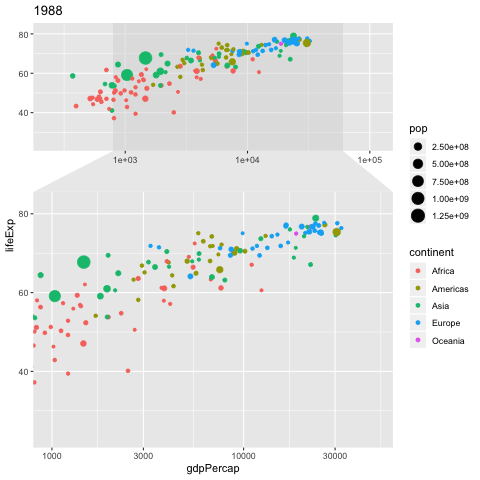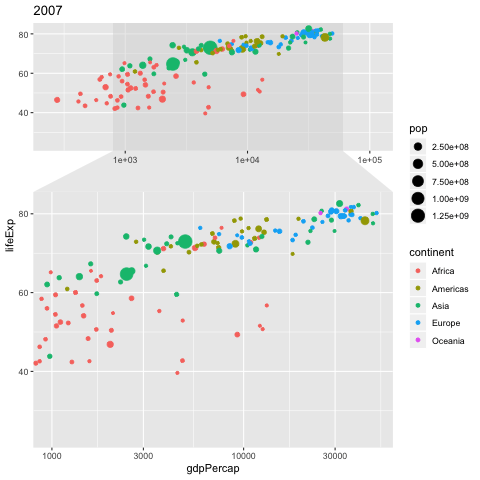
NGO Khoa Anh

I am pursing MS degree in Data Science at Sorbonne University.
Portfolio
M2 ISDS - ISUP
Complete projects for the M2 ISDS: Ingénieur Statistique et Data Science at Sorbonne University (2022-2023).
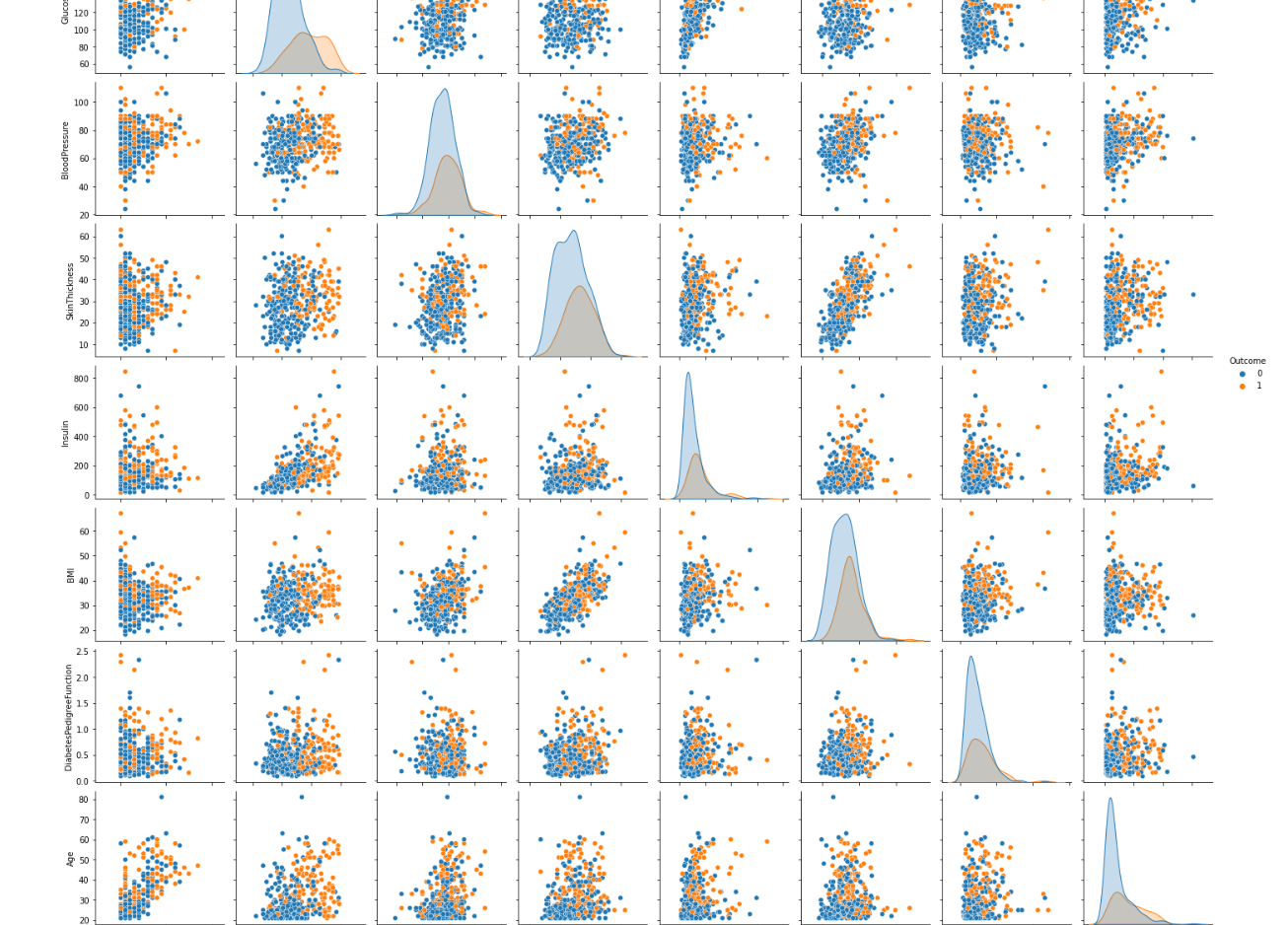
Machine Learning: Diabetes classification
In this comprehensive project, our objective is to classify diabetes using advanced Machine Learning techniques. The project initiates with a thorough analysis of the dataset, emphasizing the understanding of key variables and their relationships. This phase includes detailed data visualization and correlation studies to identify patterns and interactions critical for diabetes classification.
Subsequently, the project incorporates unsupervised learning, specifically using a K-means clustering approach, to discern distinct data groups. This methodology aims to enhance our analytical perspective and contribute to more nuanced data interpretation.
The pivotal aspect of the project involves the systematic training and evaluation of various classifiers. These include Decision Trees, Logistic Regression, Random Forest, MLP, SVM, QDA, LightGBM, Gradient Boosting, and Neural Networks. Our approach is methodical, comparing each model's performance to ascertain the most effective algorithm for our specific dataset.
The project is not only a pursuit of the optimal classification model but also an endeavor in deep learning and discovery in the field of Machine Learning.
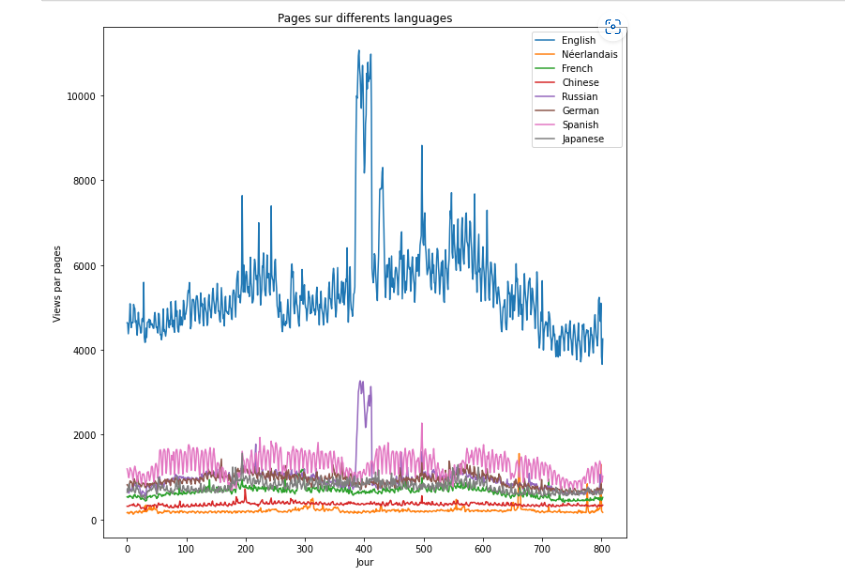
Time series: Wikipedia Traffic Forecast
This project presents a thorough investigation into the dynamics of user interactions and server performance optimization by forecasting Wikipedia page traffic. The significance of this study lies in its dual focus: gaining insights into user behavior on Wikipedia and enhancing the server performance and availability of this vast online encyclopedia. Our objective is to achieve precise predictions of Wikipedia page traffic through the application of three distinct machine learning models, each contributing uniquely to our forecasting accuracy.
[***ARIMA Model***]: Specializing in autocorrelation, the ARIMA model leverages time-series data, enabling us to make more nuanced predictions.
***XGBoost***: As a decision-tree-based ensemble machine learning algorithm, XGBoost excels in identifying complex, non-linear patterns within the data.
***Random Forest Algorithm***: Comprising multiple decision trees, this model adds an extra dimension of accuracy to our predictions.
This study provides an in-depth exploration of these machine learning models. We will demonstrate their individual capabilities and how their integrated application can significantly enhance the accuracy of traffic forecasting on Wikipedia.
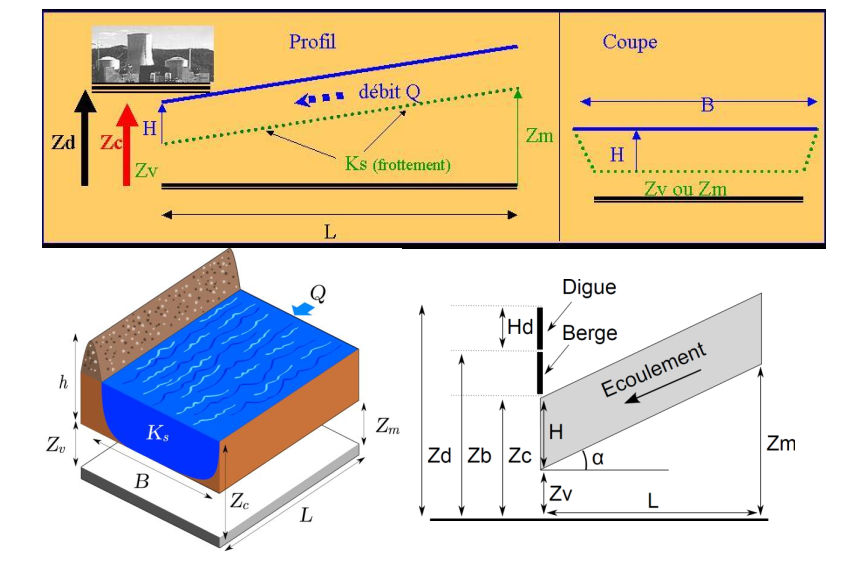
Industrial statistics
This project represents a comprehensive exploration at the nexus of industrial statistics, environmental science, and economics, targeting a pragmatic challenge in flood management. Our focus is on determining the optimal embankment heights to mitigate flood risks effectively. The foundation of our study is a robust dataset derived from real-world flood events, water flow dynamics, and economic impact assessments. The goal is to ascertain the most appropriate embankment height that not only offers adequate flood defense but also maintains economic viability. We adopt a three methodological approach, each offering a distinct perspective to analyze the data and shape our conclusions:
***Historical Measurement-Based Approach***: Leveraging historical flood data, this approach aims to utilize past measurement records as a guide for future embankment design, providing a practical, experience-based perspective.
***Hydraulic Model-Based Approach***: Here, we employ hydraulic modeling techniques to simulate water flow patterns and predict flood probabilities, offering an engineering-centric viewpoint for optimal embankment height determination.
***Economic Model-Based Approach***: This facet of our study integrates economic modeling to assess the financial implications of various embankment heights, ensuring our flood protection strategies are economically sustainable.
Through the integration of these three distinct research methodologies, our project aims to arrive at a multi-faceted solution that encapsulates a broad range of considerations, thereby ensuring a robust and comprehensive approach to flood management.
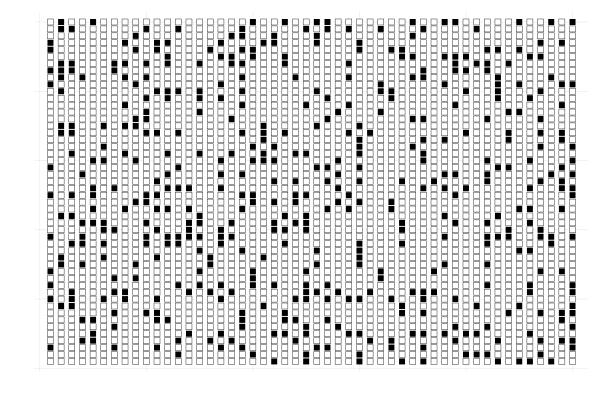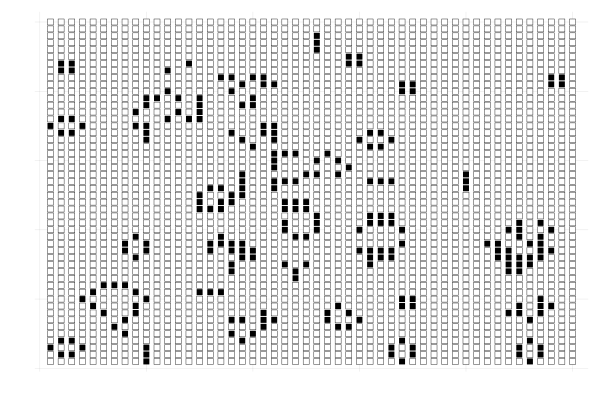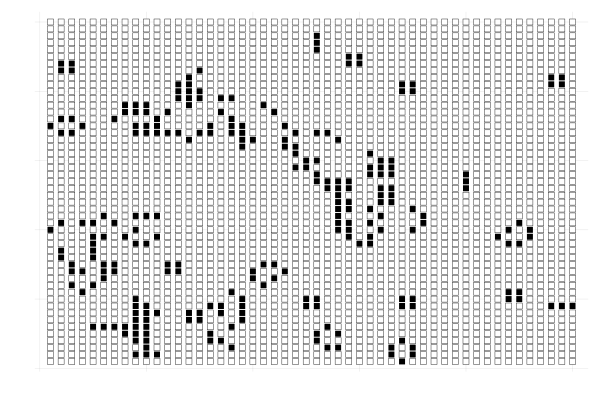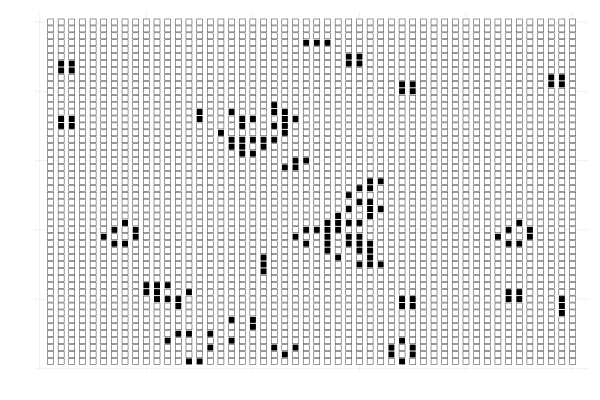
Parallel Computing: Parallel Implementation of Conway’s Game of Life
This project delves into the fascinating world of parallel computing through the implementation of Conway's Game of Life, a classical example that illustrates how simple rules can lead to complex, life-like patterns. Originally conceived by John Conway in 1970, the Game of Life is a cellular automaton played on a two-dimensional N x N grid. Each cell within this grid, representing an individual unit of life, can exist in one of two states: alive or dead. The evolution of these cells, governed by a set of local rules, simulates the processes of birth, reproduction, and death, showcasing emergent large-scale behaviors from simple interactions.
Unlike traditional games, Conway's Game of Life is an autonomous system that evolves without user input, with each cell's fate determined by its surrounding neighbors. The key feature of this project is the implementation of these evolutionary steps through parallel computing techniques. This approach involves simultaneous computation, where the state of each cell in the subsequent generation is determined independently, based on its current state and those of its eight neighbors.
Our primary objective is to effectively implement Conway's Game of Life using parallel programming paradigms. This endeavor not only serves as a technical exercise in parallel computation but also provides insights into the broader implications of local interactions in complex systems. By leveraging parallel processing, we aim to enhance the efficiency and scalability of the simulation, offering a deeper understanding of the underlying dynamics of Conway's Game of Life.
Statistical Quality Control
This project represents a rigorous exploration into the realm of manufacturing, with a specialized focus on augmenting process efficiency through the implementation of statistical quality control techniques. The core aim is to apply sophisticated statistical methodologies and adequacy tests to streamline manufacturing processes, thereby reducing waste and increasing the yield of products that meet specified quality standards.
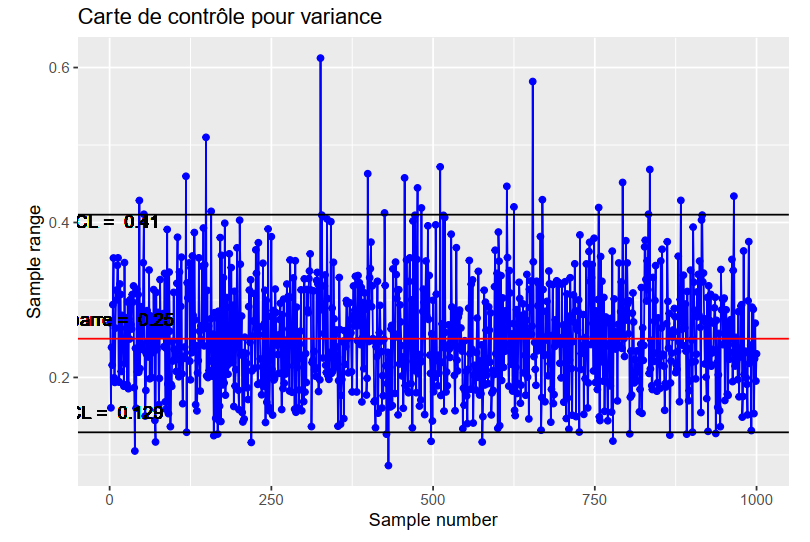
Our methodology is centered around the development and application of advanced control charts, namely the CUSUM (Cumulative Sum Control Chart) and EWMA (Exponentially Weighted Moving Average). These robust statistical instruments are pivotal in our ability to precisely identify process irregularities and effectively monitor false alarm rates.
The CUSUM chart is particularly tailored for pinpointing subtle, incremental deviations from the set process targets over time. In contrast, the EWMA chart excels in detecting more abrupt and significant shifts. This dual-chart strategy equips us with a comprehensive toolkit for scrutinizing process variability and ensuring consistent process control.
The outcomes of this project are expected to substantially refine manufacturing processes. By applying these advanced statistical control methods, we anticipate not only an optimization of the manufacturing workflow but also a significant contribution towards reducing operational waste. This project stands to deliver critical insights and methodologies, fostering more efficient, sustainable, and economically viable manufacturing operations.
Latent structure models
Kmeans and Hierarchical Ascending Classification
Objective of this project is to warn against an overly systematic or blind application of PCA in a clustering study, and to explore and compare the behavior of Kmeans and ascending hierarchical clustering.

Mixing models, Model-Based Clustering, EM algorithm
Objective of this project is first to explore the behavior of the EM in the context of a simple Gaussian mixture model at J components in dimension 1
$$
M = \{ \sum_{j=1}^J \pi_j \phi(\cdot; \mu_j, \sigma_j^2) : (\pi_1, \ldots, \pi_J) \in \Pi_J, \mu_1, \ldots, \mu_J \in \mathbb{R}, \sigma_1^2, \ldots, \sigma_J^2 \in \mathbb{R}_{+}^{*} \}
$$
$$
\text{and } \Pi_J = \{(\pi_1, \ldots, \pi_J) \in [0, 1]^J : \sum_{j=1}^J \pi_j = 1\} \text{ and } \phi(\cdot; \mu, \sigma^2) \text{ the Gaussian density of expectancy } \mu \text{ and variance } \sigma^2
$$
It is then to initiate the model-based clustering in higher dimension with the Rmixmod package, which allows to fit mixing models.
Bayesian methods, Markov Chain Monte Carlo(MCMC)
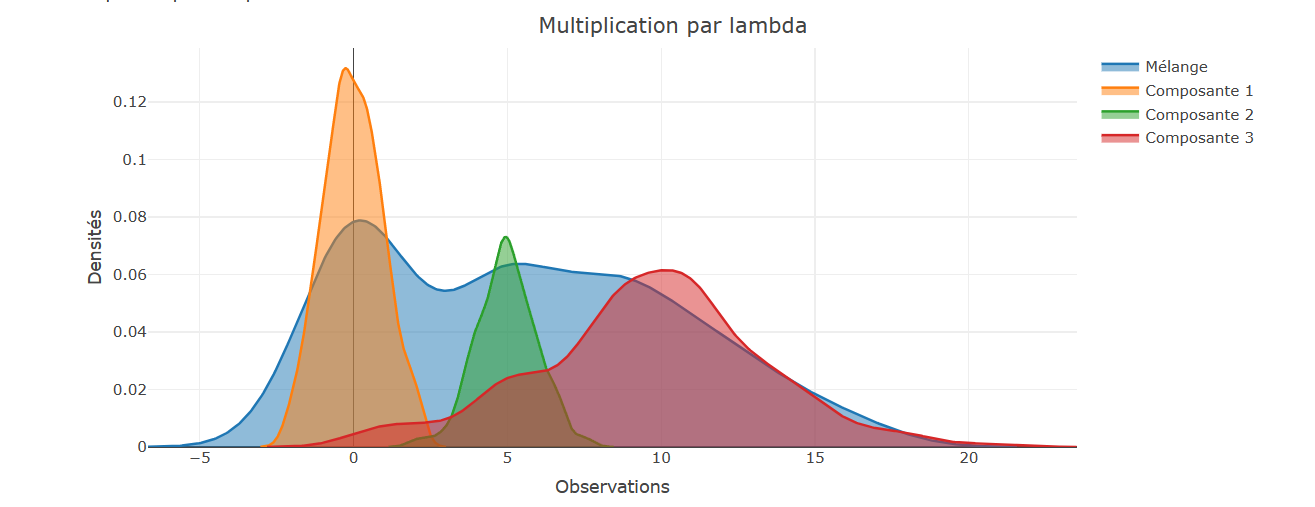
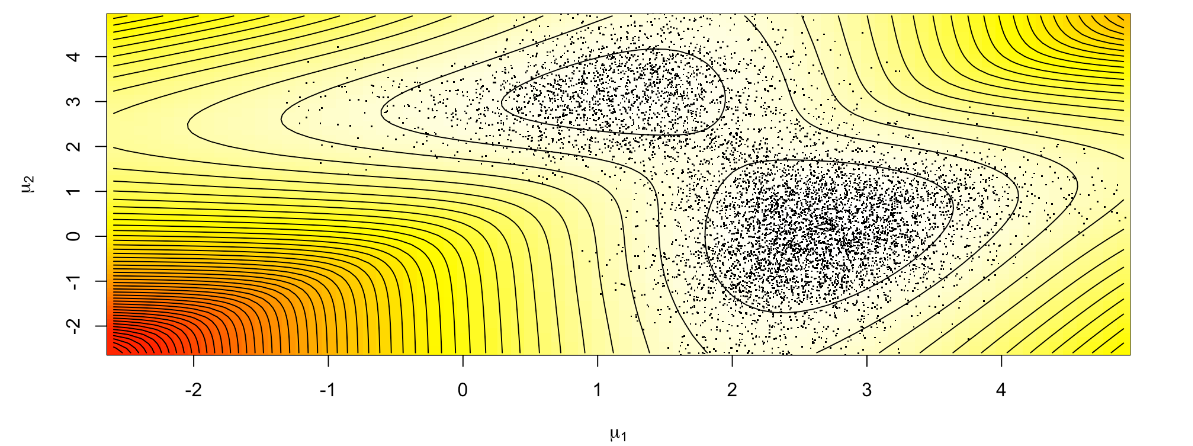
This project is an introduction to Bayesian methods in the context of Gaussian mixture models models, and in particular to the Gibbs sampler and the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm. We are interested in the following mixture model:
$$
M = \{ \pi \phi(\cdot; \mu_1, 1) + (1 - \pi) \phi(\cdot; \mu_2, 1) : \mu_1 \in \mathbb{R}, \mu_2 \in \mathbb{R} \},
$$
with $\phi$ being the Gaussian density on $\mathbb{R}$ and $\pi \neq \frac{1}{2}$ known.
The prior distribution of $(\mu_1, \mu_2)$ is given by: $\mu_1 \sim \mathcal{N}(\delta_1, \frac{1}{\lambda}), \mu_2 \sim \mathcal{N}(\delta_2, \frac{1}{\lambda}), \delta_1, \delta_2 \in \mathbb{R}$ and $\lambda > 0$, with $\mu_1$ and $\mu_2$ independent.
M1 ISIFAR: Statistical and Computer Engineering for Finance, Insurance, and Risk
Complete projects for the M1 ISIFAR: Statistical and Computer Engineering for Finance, Insurance, and Risk) at Université de Paris (2021-2022).
Asset Allocation and Portfolio Optimisation
In this project, we grapple with a classic challenge in finance: determining an investment strategy that yields optimal performance over a specified time horizon, given a set of traded assets. Our exploration takes us into the core aspects of discrete-time portfolio optimization, where the balance between risk and reward comes to the fore.
We examine three of the principal criteria in portfolio optimization to provide a comprehensive view of the problem at hand. Our methodology revolves around two potent solution strategies:
Dynamic Programming Method: A versatile approach that breaks down the larger problem into smaller, manageable sub-problems, thereby simplifying complex optimization tasks.
Martingale Method: A powerful probabilistic technique, valuable in the context of investment strategies and financial forecasting.
Further enhancing our exploration, we dive into the practicalities by providing explicit examples for both the logarithmic utility function, which captures the investor's level of risk tolerance, and the full binomial case, a method used to model the dynamics of an asset's price over time.
By undertaking this project, we aim to offer profound insights into the world of finance, contributing to more efficient, optimized investment strategies and improved financial outcomes.
SVD Analysis & Life Tables
In this captivating project, we embark on an exploration of demographic data and its intricate patterns using an array of powerful techniques. Our collaboration spans various data structures, including data.frames, tibbles, and data.tables, where we leverage the capabilities of dplyr and other query languages, such as data.table, to process and manipulate the data effectively.
With the invaluable data provided by the esteemed Human Mortality Database organization (https://www.mortality.org), we dive into a world of demographic insights. Our focus is on visualizing and analyzing multivariate datasets, with a special emphasis on life tables as an essential component of demographic research.
To unravel the underlying trends and uncover hidden patterns, we employ a range of powerful techniques, including Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) analysis and Principal Component Analysis (PCA). These matrix-oriented methods provide a comprehensive understanding of the interrelationships and variations within the data.
Moreover, we delve into the application of the renowned Lee-Carter model, a widely accepted methodology for predicting mortality quotients. This model not only aids in forecasting future mortality trends but also plays a crucial role in informing public health policies and insurance industry practices.
By combining statistical analysis, data manipulation, and advanced modeling techniques, this project offers profound insights into demographic dynamics, contributing to our understanding of population trends, mortality patterns, and the intricate interplay between various demographic factors.